Daylight Saving Time: How It Started and Changed Over the Years
By: Wise News Network Staff
Daylight Saving Time (DST) is when we set our clocks forward by one hour in the spring and set them back by one hour in the fall. The main idea behind this change is to make better use of daylight during the longer days of summer. But why do we do this?
A Bit of History
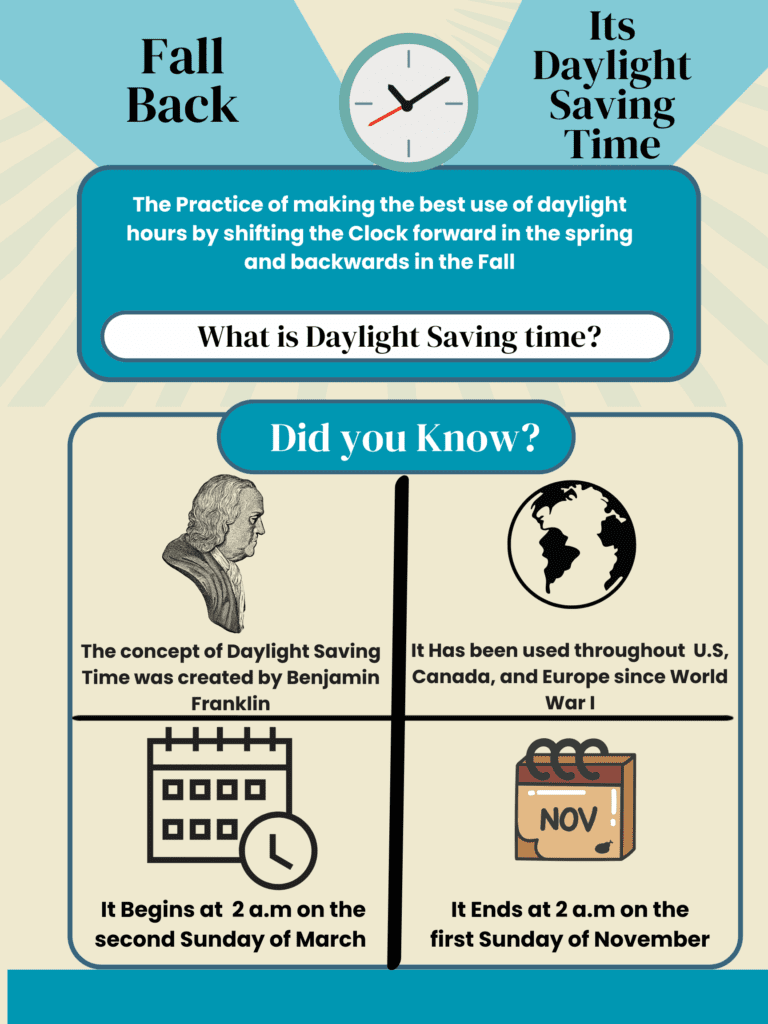
Daylight Saving Time dates back to the late 1700s when Benjamin Franklin suggested it as a way to save energy. However, it didn’t take off until World War I, when Germany started using it to save fuel. The United States followed suit in 1918, but after the war, it was dropped. DST came back during World War II. In 1966, the U.S. government made rules for when DST would start and end: the second Sunday in March and the first Sunday in November.
During the oil embargo of 1973, Congress in the United States implemented year-round daylight saving time as a measure to conserve energy. This initiative lasted from January 1974 until April 1975 but proved to be ineffective in saving energy and quickly lost popularity. By October 1974, the country reverted to standard time.
From 1987 to 2006, daylight saving time began on the first weekend of April and continued until the last weekend in October.
In 2007, the dates for daylight saving time were changed once more. It now starts on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first Sunday in November, a schedule that remains in place today.
The Purpose of Daylight Saving Time
The main goal of DST is to make better use of daylight. By moving an hour of daylight from the morning to the evening, people can spend more time outside after work or school. This change is also supposed to save energy, as longer daylight hours mean less need for electric lights at night.
For more WNN video news stories, visit YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@wisenewsnetwork
For more WNN articles and news stories, visit: https://wisenewsnetwork.com
Contact WNN at [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Wise News Network. All rights reserved.
